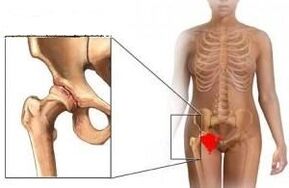
The osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a serious pathology that develops in the hip joint as a result of nutrition and, as a result, the destruction of the cartilage tissue and the immobility of the thigh.
With a healthy cartilage tissue of the joint, the movement occurs easily and does not cause any inconvenience.If the cartilage is damaged by osteoarthritis, then its surface is no longer smooth, it has a zabina, a pit that hinders the normal flexion/extension of the joint.The thigh becomes like the rusty loops of a garden door, in the opening of which a crunch is heard and feels tension when it moves.
The disease is dangerous because with the inopportune beginning of the treatment, the cure is not only impossible, but the course of the disease leads to greater immobility and joint loss.
Causes
What is it?Cooksarrosis develops for many reasons, the main one is a sedentary lifestyle.Very often, athletes suffer from this ailment due to large loads that can damage the joint.Unfortunately, osteoarthritis is often inherited, a congenital dislocation in the inguinal region is possible.
The reasons that cause the development of cookyrosis of the hip joint:
- Allow disease;
- fracture of the thigh neck;
- receive injuries or microtrauma in childhood;
- Excess weight, high load;
- drink alcohol;
- congenital diseases;
- higher levels of hormones (age -related changes);
- tissue inflammation;
- destruction of joint tissues;
- taking powerful drugs;
- stressful situations;
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- Pathological thigh diseases in the inguinal region.
Special attention should be paid to the presence of injuries (microtrauma).They cure for a long time, which leads to the development of the disease for years.Most of the time, the disease begins to develop in people 40 years or more.Inflammation begins with a hip joint, but if it does not take timely treatment, the disease applies to other areas.
Symptoms of the arthrohrosis of the hip joint
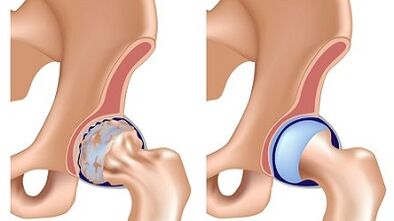
Cooksarrosis develops more frequently in people over 40 years.Gradually progresses and the condition of a person worsens from one year to another.If the damaged articulation is not treated, after some time pathological changes can occur in another joint.
In world practice, it is recognized that the osteoarthritis of the hip joint has three stages or stages of development.Each of them is characterized by their own symptoms.
1 Degree of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
At this stage of the disease, a person experiences pain only with and after physical effort, to run or walk prolonged, while mainly the joint hurts, the pain is rarely gives pain to the thigh or knee.
In addition, at the same time, the march in a person is ordinary, no chroma is observed, the hip muscles are not stunted.As the images diagnose, bone growth is observed, which are around the internal and external edge of the acetabulum, no other pathological disorders in the neck and head of the femur are observed.
2 degrees of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
With the osteoarthritis of the second degree of the hip joint, the symptoms become significant and the pain already acquires a more constant and intense nature, and at rest and when they move, they both give in the groin and in the thigh, in the load, the patient is already limbing.There is also a restriction of the thigh, the volume of hip movements is reduced.
In the images, the narrowing of the gap becomes half of the norm, the bone growths are found outside and on the internal edge, the head of the hip head begins to increase, deform and move up, its edges become unequal.
3 degrees of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
At this stage of the disease, pain is constant painful in nature, both day and night, the patient becomes difficult to move independently, so a cane or crutches is used, the volume of joint movement is very limited, the muscles of the lower part of the leg, hips and buttocks are the traffic.
The leg is shortened and the person is forced to bow the body when walking towards the sick leg.From the displacement of the center of gravity, the load in the damaged joint increases.In X -ray images, multiple bone growths are found, the head of the thigh expands and the joint gap is significantly reduced.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on Anamnesis data (identification of risk factors or causal diseases), additional clinical data and exam methods.
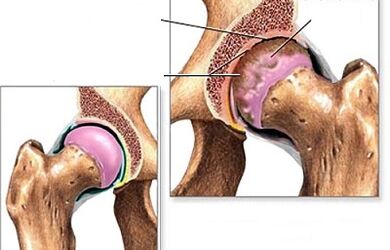
To clarify the diagnosis and drive the differential diagnosis, it will help:
- X -Ray of the hip joints;
- Articulations ultrasound;
- MRI or CT.
As a general rule, to establish a precise diagnosis, a sufficiently clinical and radiological examination.In radiographs, specific characteristic changes of each stage of the disease are found: narrowing of the joint gap, the presence of osteophytes, displacement and deformation of the femoral head, subcondral cysts and periarticular osteosclerosis, osteoporotic changes in the bones.Depending on the presence of these pathological changes and their severity, the degree and stage of the disease are established.
Treatment of hip joint osteoarthritis
In the first stage, the osteoarthritis of the hip joint lends itself to the conservative treatment.The primary task is to relieve pain, which prevents the patient from moving.
In the process of coxarthrosis therapy,:
- Restoration of nutrition and blood circulation in muscle and cartilage;
- Physical activity in the damaged joint decreases;
- Restoration of damaged cartilage;
- activation of hidden reserves of the human body, which will contribute to the regeneration of the tissue at the microcellular level;
- increase in the joint gap;
- Restoring the mobility of the joint.
During pharmacological treatment, this category of patients, the following medications are prescribed:
- Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory.They will help eliminate pain, eliminate formed edema and inflammation, however, its un controlled use will contribute to the suppression of the natural possibility of cartilage to restore.Doctors do not recommend using more than one non -steroidal medication simultaneously;
- Relaxing muscles.Remove muscle cramps, increase blood supply in the joints, but its use must take place under the supervision of a doctor due to side effects;
- Expanding ships.They are able to relax smooth muscles and increase space between the muscles.Have a minimum of contraindications, but its effectiveness is an individual indicator;
- Type of steroids.Help with concomitant diseases such as the presence of inflammation of the thigh bone, but has many side effects;
- Restoring the cartilage.Condroprotectors are the most useful for cure to deform osteoarthritis.They feed the cartilage with the desired elements and stop the development of the disease;
- Local use.The main positive effect lies in the process of rubbing products on the skin, which relieves muscle cramps and helps improve blood circulation.
During conservative treatment, patients should adhere to the diet, specially designed for patients with osteoarthritis of the hip joint.The course of therapy therapy includes a therapeutic massage, which is shown in patients with 1 and 2 stages of osteoarthritis.
Endoprotetics
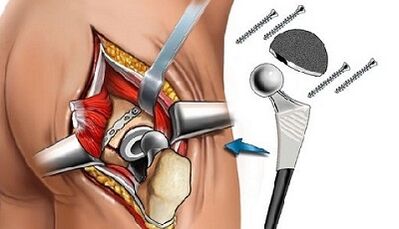
The third stage of the disease lends itself only to surgical treatment.The patient is recommended to replace the joint or endoprothetic.The surgeon cuts the head of the thigh bone, inserts a metal pin into the cut, in which it holds the artificial head.
The prosthesis itself is a single power (replacing only the head) and total (replacing both components).The next day after the operation, some elements of exercise therapy are performed in a lie in bed, the patient can stand up, but so far without leg support, after a few days with crutches.After 2-3 months, crutches will not be needed, a full leg will be allowed.
Patients who have undergone endoprothetic for rehabilitation, which consist of physiotherapy exercises, a massage and physiotherapy course are recommended.In most cases, the function of the extremities is restored.The life of the prosthesis is 10 to 20 years, then it is replaced by a new one.
Gymnastics with osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Exercises for the fight and prevention of cookyrosis must be carried out carefully.The movement for exercise therapy should be soft, do not cause pain.LFK for the treatment of the disease must be aimed mainly to strengthen the muscles themselves and not load the joints.A good way to prevent cookardisis is swimming, especially in salt water.
- Initial position: Lie on the floor, stretch your arms and legs along the body.Slowly, lift your painful leg straightened in the knee joint 15 cm from the floor and hold it for approximately half a minute.After that, lower the leg and repeat the exercise with another foot;
- Initial position: Lie on the stomach, legs and arms stretch along the body.Lift your legs straight 15 cm, do and then extend them to the sides.Everything must be done slowly.
The patient must remember that some exercises with osteoarthritis of the hip joint of exercise therapy can be difficult for him due to his physical training.They are quite effective methods for the prevention of several ailments, therefore, they are included in the exercise therapy system both with osteoarthritis and other diseases.
Popular remedies
In Popular Medicine, there are many successful methods to treat coxarcherosis:

- Tinturas and decoctions used (there are many recipes for the preparation of healing popular medicines, including garlic, lemons, mummies and various parts of plants, and honey, and so on);
- Ointments based on several natural components (ointments made of cell phone, eucalyptus oil, aloe and other plants);
- Compresses and bathtubs (imposition of cabbage sheets, bathrooms with jerusalem artichoke, etc.).
Applying all popular remedies, it should be remembered that the guarantees of a 100 percent recovery do not exist.
Prevention
The prevention measures are very important, especially if it had a history of dysplasia of the hip joint, fractures, strong bruises or purulent processes in this area.
- Body weight control (reduces the use of flour, table salt, sweet, tea and coffee products in the diet).With overweight, it increases the risk of osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
- Exception of weight transfer, jumps (especially from heights).Try not to stand for a long time.
- If there are diseases associated with metabolism (diabetes, atherosclerosis), they should be compensated.
- Physical exercises dosed to strengthen the muscles of the hips and buttocks (cycling or cycling, swimming, therapeutic gymnastics).
Compliance with preventive measures, early detection of coxarche and its proper treatment is the key to a positive prognosis in this disease.























